Applications of Vacuum and Oil Circuit Breaker: Which One to Choose?
Date: February 18th, 2026
In the world of electrical engineering, circuit breakers play a crucial role in protecting electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads, short circuits, or faults. Among the various types of circuit breakers, vacuum circuit breaker and oil circuit breaker are two of the most commonly used types. Each has its own set of advantages, applications, and considerations for usage. In this blog, we’ll delve into the differences between these two types of circuit breakers, their applications, and help you choose the best one for your needs.
What is a Vacuum Circuit Breaker?
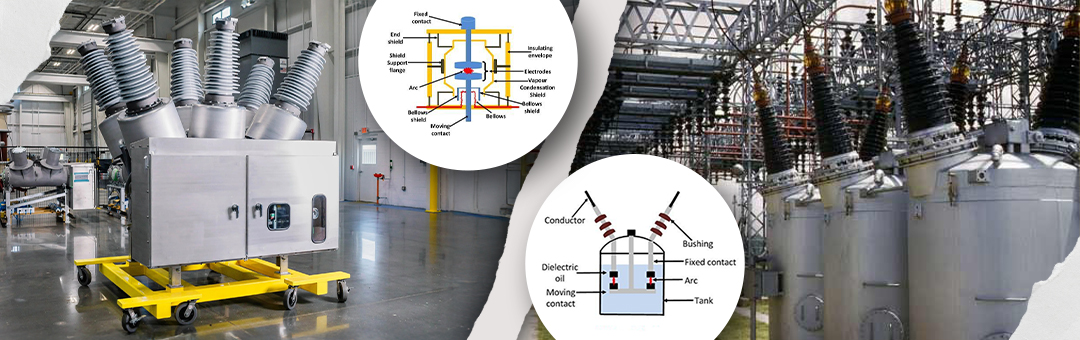
A vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) uses a vacuum as the arc-extinguishing medium. In this type of breaker, when the contacts open to interrupt the current, the arc formed is quickly extinguished within the vacuum. The vacuum helps prevent the ionization of the medium, ensuring that the arc does not reignite once it is broken. Vacuum circuit breakers are often used for low- and medium-voltage applications.
What is an Oil Circuit Breaker?
An oil circuit breaker (OCB) uses oil as the arc-extinguishing medium. When the contacts of the breaker separate during a fault condition, the electric arc that is generated is cooled and extinguished by the oil. The oil serves not only as an insulating medium but also as a coolant. Oil circuit breaker are typically used in high-voltage applications, though their use has declined with the advent of more modern technologies such as vacuum circuit breakers.
Comparison Between Vacuum and Oil Circuit Breaker
To understand which circuit breaker is more suitable for your application, let’s break down the key differences between vacuum and oil circuit breakers.
-
Arc Extinguishing Medium
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: As the name suggests, vacuum circuit breakers rely on vacuum as the arc-extinguishing medium. The absence of air and the highly effective dielectric properties of the vacuum help to quickly quench the arc.
- Oil Circuit Breakers: This use oil to cool and quench the arc. The oil also serves as an insulator for the electrical components within the breaker.
-
Voltage Rating
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: VCBs are typically used for low to medium voltage applications, ranging from 11 kV to 36 kV, although newer designs have pushed the voltage limits higher.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: OCBs are suitable for higher voltage applications, generally above 36 kV and even up to 800 kV, making them ideal for power transmission and distribution systems.
-
Speed and Efficiency
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: VCBs have faster operation times compared to oil circuit breaker. The arc quenching process is more efficient, and the time it takes to open and clear a fault is minimal, improving the overall reliability of the electrical system.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: OCBs are slower in operation due to the more complex process of arc quenching and oil cooling. The arc quenching process takes longer, making it less efficient than VCBs in certain scenarios.
-
Maintenance
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: VCBs are low-maintenance. The vacuum inside the breaker does not require any refilling or regular servicing, as it remains sealed and unaffected by external conditions.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: OCBs require periodic maintenance due to the need to inspect the oil level, replace it, and ensure that the oil does not degrade over time. Additionally, OCB’s are prone to issues related to the oil insulation, especially if it becomes contaminated.
-
Environmental Impact
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: VCBs are considered more environmentally friendly, as they do not involve the use of any hazardous or harmful materials. They have a minimal environmental footprint.
- Oil Circuit Breakers: It can have a significant environmental impact due to the use of oil, which is flammable and can leak or spill, causing pollution. This makes OCBs less desirable in environmentally-conscious industries.
-
Cost
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: VCBs tend to be more cost-effective for medium-voltage applications due to their lower maintenance and simpler construction. However, their initial cost can sometimes be higher compared to OCB, especially for high-voltage applications.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: OCBs are more expensive to maintain, particularly in terms of oil replacement and servicing. They are also more expensive in terms of installation due to their larger size and the need for a specialized environment to store the oil.
Applications of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
-
Low and Medium Voltage Power Systems
- VCBs are commonly used in low and medium-voltage circuits, such as distribution networks, industrial facilities, and substations. They are ideal for environments where rapid arc quenching is essential.
- VCBs are commonly used in low and medium-voltage circuits, such as distribution networks, industrial facilities, and substations. They are ideal for environments where rapid arc quenching is essential.
-
Industries with Frequent Switching
- VCBs are commonly used in industries where the switching frequency is high. Due to their fast action and low maintenance needs, VCBs are perfect for systems that need to handle frequent load shedding or switching operations.
- VCBs are commonly used in industries where the switching frequency is high. Due to their fast action and low maintenance needs, VCBs are perfect for systems that need to handle frequent load shedding or switching operations.
-
Renewable Energy Systems
- With the rapid adoption of renewable energy sources like wind and solar, VCBs are finding increasing use in these applications to manage fault conditions and ensure efficient power distribution.
- With the rapid adoption of renewable energy sources like wind and solar, VCBs are finding increasing use in these applications to manage fault conditions and ensure efficient power distribution.
Applications of Oil Circuit Breakers
-
High Voltage Transmission Networks
- OCBs are most often used in high-voltage transmission networks and power plants, particularly in systems where switching under load and high fault clearing capacity is required.
- OCBs are most often used in high-voltage transmission networks and power plants, particularly in systems where switching under load and high fault clearing capacity is required.
-
Heavy Duty Industrial Applications
- Large industries with heavy machinery and high electrical demand often use OCBs for their high-voltage needs. These industries include mining, oil & gas, and large manufacturing plants.
- Large industries with heavy machinery and high electrical demand often use OCBs for their high-voltage needs. These industries include mining, oil & gas, and large manufacturing plants.
-
Substations and Power Plants
- OCBs are used extensively in power stations, electrical substations, and other areas requiring significant power transmission where quick recovery from faults is essential.
- OCBs are used extensively in power stations, electrical substations, and other areas requiring significant power transmission where quick recovery from faults is essential.
Which One Should You Choose?
When deciding between a vacuum circuit breaker and an oil circuit breaker, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of your electrical system. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- If you are working with low- to medium-voltage systems, require faster operation, and prefer lower maintenance, vacuum circuit breakers are the way to go.
- If you are dealing with high-voltage transmission systems, require higher breaking capacity, and can afford the maintenance, then oil circuit breakers might be your best bet.
Choose Anand Steemet Pvt. Ltd. for Your Circuit Breaker Needs
When it comes to selecting the right circuit breaker for your electrical system, it is crucial to choose a reliable and knowledgeable partner. Anand Steemet Pvt. Ltd. offers a wide range of high-quality vacuum and oil circuit breakers tailored to meet the needs of different industries and voltage systems. With years of expertise in providing efficient and durable solutions, Anand Steemet Pvt. Ltd. ensures that your electrical infrastructure is safeguarded with the best technology. Trust them for expert advice, product reliability, and unparalleled customer service.